
- Uncategorized
- August 30, 2022
- No Comments
Incremental Cost of Capital: Definition, Overview & Example

Suppose a company wants to reduce its carbon footprint by switching to renewable energy sources. They need to compare the additional costs (solar panels, wind turbines, and grid integration) https://www.bookstime.com/articles/how-to-record-a-credit-sale against the incremental benefits (lower energy bills, positive brand image, and environmental impact). Remember, comparing benefits and costs is not a one-size-fits-all approach.
- If the total production cost for 9,000 widgets was $45,000, and the total cost after adding the additional 1,000 units increased to $50,000, the cost for the additional 1,000 units is $5,000.
- Several factors can influence incremental costs, and it is crucial to consider them when analyzing different options.
- From an individual standpoint, incremental cost plays a significant role in personal decision making.
- Incremental cost determines the change in costs if a manufacturer decides to expand production.
Incremental Cost of Capital: Definition, Overview & Example
Incremental costs are relevant in making short-term decisions or choosing between two alternatives, such as whether to accept a special order. If a reduced price is established for a special order, then its critical that the revenue received from the special order at least covers the incremental costs. For any business decision that involves changing volumes or adding products/services, incremental costs are vital for determining the financial impact. Companies invest in marketing campaigns to promote their products or services.
Comparing Benefits and Costs
Sensitivity analysis is a technique used to assess the impact of changes in key variables on the overall outcome of a decision or project. It helps us understand how sensitive the results are to variations in these variables. By systematically varying the values of these variables, we can gain insights into the robustness and reliability of our calculations. Remember, identifying relevant costs requires a holistic approach, considering both short-term and long-term implications. By mastering this skill, decision-makers can make informed choices that maximize value and drive success.
Incremental Costs Vs Margin Costs
If a company responds to greater demand for its widgets by increasing production from 9,000 units to 10,000 units, it will incur additional costs to make the extra 1,000 widgets. If the total production cost for 9,000 widgets was $45,000, and the total cost after adding the additional 1,000 units increased to $50,000, the cost for the additional 1,000 units is $5,000. Before calculating ICC, you need to determine the fixed costs and the variable costs. Fixed costs are those that do not change with production or sales, such as incremental cost rent and insurance.

Incremental costs are a vital concept in business and finance, helping organizations make informed decisions about resource allocation, pricing strategies, and profitability. Let’s explore what incremental costs entail, their significance in business operations, and provide examples to illustrate their application. Incremental cost, often referred to as “marginal cost,” represents the change in total cost resulting from producing one additional unit of a product or service. It’s the cost incurred beyond the status quo—a shift from the familiar to the slightly altered.
Understanding Incremental Costs in Business

Incremental cost analysis is used when making investment decisions. It takes into account all relevant costs and benefits when making investment decisions. This is because fixed costs are not relevant to the decision of whether or not to pursue a new project or venture.
However, the $50 of https://x.com/BooksTimeInc allocated fixed overhead costs are a sunk cost and are already spent. The company has excess capacity and should only consider the relevant costs. Therefore, the cost to produce the special order is $200 per item ($125 + $50 + $25). It can be of interest to determine the incremental change in cost in a number of situations. For example, the incremental cost of an employee’s termination includes the cost of additional benefits given to the person as a result of the termination, such as the cost of career counseling. Or, the incremental cost of shutting down a production line includes the costs to lay off employees, sell unnecessary equipment, and convert the facility to some other use.
What is an incremental cost?
- Forecast LRIC is evident on the income statement where revenues, cost of goods sold, and operational expenses will be affected, which impacts the overall long-term profitability of the company.
- To finance a new project, for example, it may need to take on debt or sell more equity.
- In this section, we will delve into the intricacies of comparing benefits and costs, providing insights from various perspectives.
- You then subtract the variable costs of making one widget from the variable cost of making two widgets.
- Producing the products, however, might bring incremental costs because of the downsizing.
To increase the sales to gain more market share, the company can leverage the lower cost per unit of the product to lower the price from ₹ 25 and sell more units at a lower price. The basic method of allocation of incremental cost in economics is to assign a primary user and the additional or incremental user of the total cost. Like in the above example, it is evident that the per-unit cost of manufacturing the products has decreased from ₹ 20 to ₹ 17.5 after introducing the new product line.

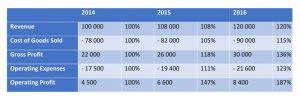
The company management can consider the cost of producing one additional unit to make their pricing decisions to make a profit. Incremental costs (or marginal costs) help determine the profit maximization point for an organization. If a business is earning more incremental revenue (or marginal revenue) per product than the incremental cost of manufacturing or buying that product, the business earns a profit.
